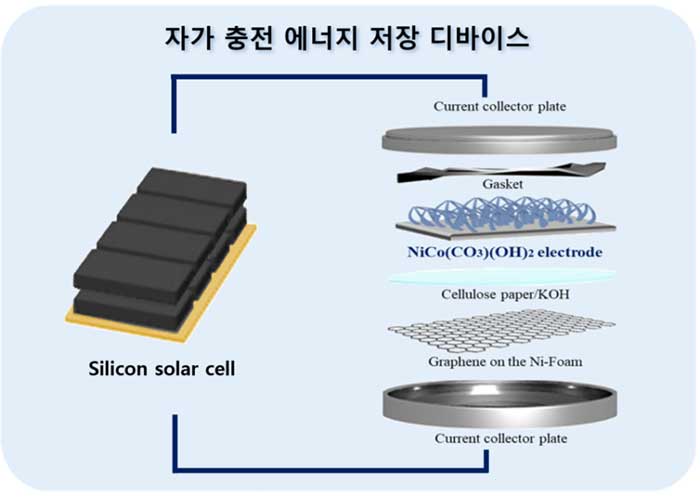
In a significant scientific breakthrough, researchers from South Korea have developed a self-charging energy storage device that combines supercapacitors with solar cells. This innovative technology, led by Senior Researcher Jeongmin Kim at DGIST (Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology) and Damin Lee from Kyungpook National University, promises to revolutionize sustainable energy solutions. The device utilizes novel electrode materials and achieves impressive energy and power densities, making it a potential game-changer in the field of energy storage.
Innovative Electrode Design
The key to this breakthrough lies in the innovative electrode design. The researchers used a nickel-based carbonate and hydroxide composite material, enhanced with transition metal ions such as manganese (Mn), cobalt (Co), copper (Cu), iron (Fe), and zinc (Zn). This combination maximizes both conductivity and stability, significantly boosting the energy and power densities of the device. The energy density achieved is 35.5 watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg), which is significantly higher than previous studies that achieved only 5-20 Wh/kg. The power density is an impressive 2555.6 watts per kilogram (W/kg), far exceeding earlier achievements of around 1000 W/kg.
Combining Supercapacitors with Solar Cells
One of the most notable aspects of this technology is the integration of supercapacitors with silicon solar cells. This combination allows the device to store solar energy and utilize it in real-time. The system achieved an energy storage efficiency of 63% and an overall efficiency of 5.17%, validating its potential for commercial applications. This means that the device can efficiently capture and store solar power, providing a reliable and sustainable energy source.
Long-Term Usability and Stability
The performance of the device showed minimal degradation during repeated charge and discharge cycles, confirming its long-term usability. This is crucial for practical applications, as it ensures that the device can maintain its performance over time without significant wear and tear. The stability of the charge and discharge cycles is a testament to the robustness of the electrode materials and the overall design of the device.
Potential for Commercialization
The research team believes that this technology has strong potential for commercialization. By overcoming the limitations of traditional energy storage devices, the self-charging energy storage device presents a sustainable solution for energy storage. The team plans to conduct further research to improve the efficiency of the device and explore its commercial viability. This could lead to the development of faster-charging, longer-lasting energy storage systems that can be used in various applications, from consumer electronics to large-scale renewable energy projects.
Conclusion
The breakthrough solar-powered charging technology developed by Korean scientists represents a significant advancement in the field of energy storage. By combining supercapacitors with solar cells and utilizing innovative electrode materials, the researchers have created a device that excels in energy density, power density, and stability. This technology has the potential to pave the way for more efficient and sustainable energy solutions, contributing to the global effort to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and mitigate climate change. As research continues, the commercialization of this technology could bring about a new era of renewable energy storage, benefiting both the environment and society.
Citation
https://scienceblog.com/552752/korean-scientists-develop-breakthrough-solar-powered-charging-tech/